Webb Space Telescope’s first full-color images of distant galaxies revealed
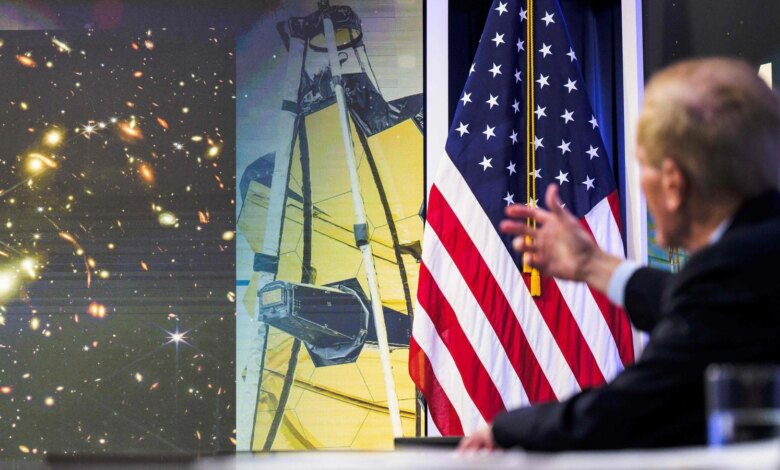

Webb’s first full-color, high-resolution snapshot of the White House came on the eve of the release of larger spectral data and photos.
Our President Joe Bidenpause in the face of political pressures to bask in the light of The universereleased the first photo from NASA’s James Webb Space on Monday Telescope – image of a galaxy cluster reveals the most detailed view of the early universe ever seen.
The White House’s sneak peek of Webb’s first full-color, high-resolution image emerged the night before the larger announcement of Webb. Photograph and spectral data NASA plans to introduce Tuesday at the Goddard Space Flight Center in suburban Maryland.
The $9 billion Webb Observatory, the largest and most powerful space science telescope ever launched, is designed to peer across the universe to the dawn of the known universe, ushering in an era revolution in astronomical discovery.
Image presented by Biden and NASA Director Bill Nelson shows a 4.6-billion-year-old galaxy cluster called SMACS 0723, whose combined mass acts as a “gravitational lens”, distorting space to significantly magnifies the light coming from galaxies further behind it.
At least one The older, faint light specifications that appear in the photo’s “background” – a composite of images with different wavelengths of light – date back more than 13 billion years, Nelson said. That makes it just 800 million years younger than the Big Bang, the theoretical flashpoint that puts the known expansion of the universe in motion about 13.8 billion years ago.
“It’s a new window in the history of The universe“, Biden said before the photo was released. And today we’re going to look at the first light coming through that window: light from other worlds, from orbit stars far beyond ours. That was amazing to me. “
He was joined in the former Executive Office Building of the White House complex by Vice President Kamala Harris, Who President of the US National Space Council.
FROM THE SAND OF THE SKY
On Friday, the space agency posted a list of five celestial objects selected to showcase Webb’s debut. These include SMACS 0723, a jewel-like sliver of the distant universe that, according to NASA, provides “the most detailed view of the early universe to date.” It also forms the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe ever taken.
Thousands of galaxies captured in a tiny patch of sky roughly the size of a grain of sand held by someone standing on it The earthNelson said.
Webb was built under contract by aerospace giant Northrop Grumman Corp. It was launched into space for NASA and its European and Canadian partners on Christmas Day 2021 from French Guiana, on the northeastern coast of South America.
The highly anticipated first image release follows six months of remotely opening Webb’s various components, aligning its mirrors and correction instruments.
With Webb now refined and fully focused, scientists will embark on a competitively selected list of missions exploring the evolution of galaxies, life the cycles of the stars, the atmospheres of distant planets and our outer moons solar system.
Built to observe objects primarily in the infrared spectrum, Webb is about 100 times more sensitive than its 30-year-old predecessor, the Hubble Space Telescope, which operates primarily at optical and optical wavelengths. ultraviolet ray.
The much larger light-collecting surface of Webb’s main mirror – an array of 18 hexagonal segments of gold-coated beryllium – allows it to observe objects at greater distances, going further back in time than with Hubble or any other telescope.
All five of Webb’s introductory goals were previously known to scientists. Among them are two giant clouds of gas and dust that are blasted into space by stellar explosions to form incubators for new stars – the Carina Nebula and the Southern Ring Nebula, each thousands of miles from Earth. light year.
The collection also includes a cluster of galaxies known as Stephan’s Quartet, which was first discovered in 1877 and includes a number of galaxies described by NASA as “locked up in the cosmic universe of those galaxies.” close encounters again and again.”
NASA will also present Webb’s first spectroscopic analysis of an exoplanet – half the mass of Jupiter located more than 1,100 light-years away – revealing molecular signatures of filtered light passing through. its atmosphere.