As biodiversity degrades, natural solutions are lost forever

United Nations Conference on Biodiversity, COP15which ends on December 19. This weekend, we’ll look at some of the ways that humanity depends on biodiversity for a healthy and thriving global ecosystem.
When a species goes extinct, it takes with it all the physical, chemical, biological and behavioral attributes that have been selected for that species, after being tried and tested again in countless experiments. evolved over thousands, and perhaps millions, of years of evolution.
These include designs for heating, cooling and ventilation; to be able to move most efficiently and effectively through water or air; for energy production and storage; to create the strongest, lightest, most biodegradable and recyclable materials; and for many, many other functions essential to life.
The value of nature is not limited to human applications, but the loss of nature and biodiversity is also great damage to human potential.
Here are some examples of the ways that nature has inspired engineering solutions.
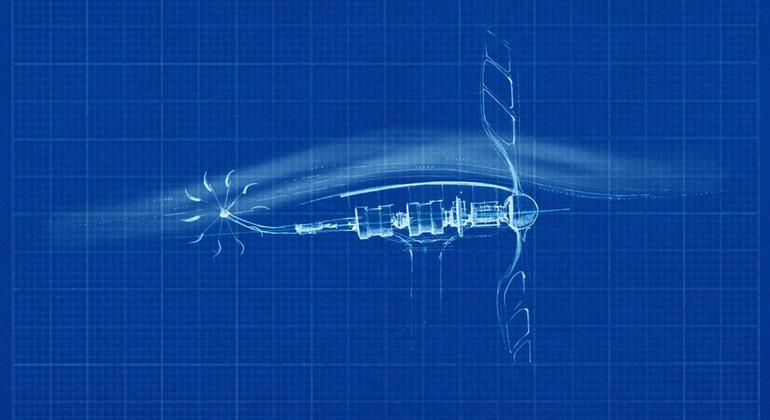
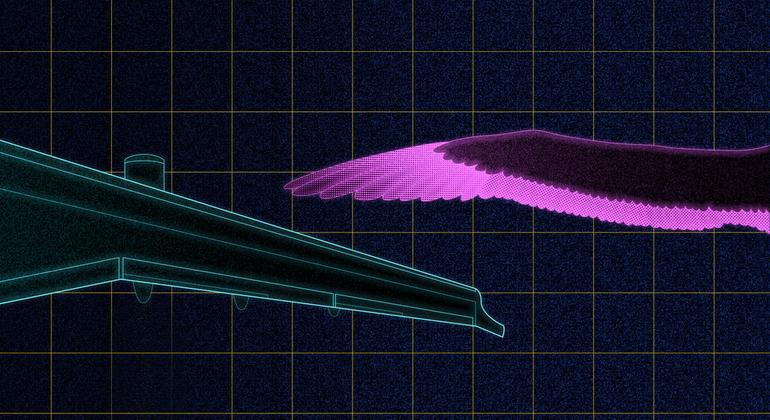
Dragonfly’s path
Inspired by the energy efficiency of dragonfly wings, especially at low wind speeds, Professor Akira Obata, formerly from Japan’s Nippon Bunri University, designed corrugated blades for super wind turbines. small spin and generate electricity, at wind speeds as low as 3 kph.
Most wind turbines perform poorly when the speed is less than 10 kph; some won’t turn at all. By lowering minimum wind speed requirements, these micro wind turbines can harness wind energy in easily accessible locations such as roofs and balconies, and without the need for expensive towers. money to obtain higher wind speed at higher altitudes.
By studying and understanding the aerodynamics of dragonfly flight, Obata was able to create ultra-small, light, stable and efficient wind turbines that can be used in off-grid locations. electricity in developing countries.
What is blacker than black?
Some butterflies, birds and spiders have evolved a super-black color achieved by complex light-trapping mechanisms that could lead to new energy-efficient designs for capturing solar energy.
The micro and nanostructure of surfaces strongly determines their light absorption or reflection properties. Understanding not only the composition of the pigments involved, but also the fine structure and physical properties of these surfaces, could be helpful in designing more energy efficient systems for heating and cool buildings as well as solar collectors more efficiently.
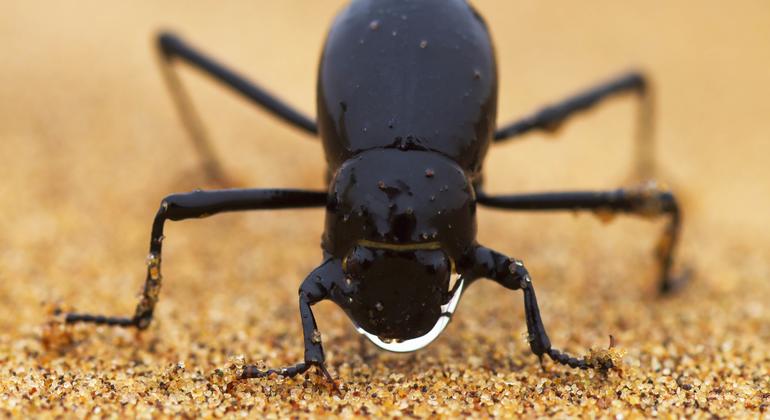

‘Immerse yourself in the fog’
The two species of beetles actively extract water from the fog by a sequence of behaviors known as ‘fog filling’. Late at night, before the nightly fog sets in in the coastal regions of the Namib Desert, these bugs emerge from the sand and climb up the dunes to place themselves in the mist’s path.
Leaning forward while facing fog, they attract moisture on their backs, which are made up of stiff front wings called elytras that cover and protect their hind wings, used for flight.
Small droplets of water in the fog gather there, combining to form larger droplets that, by gravity, run down smooth hydrophobic (i.e. impermeable) surfaces to reach the beetle’s mouth.
Send WHO Estimated that half of the world’s population will live in a water-stressed environment by 2025, the specific structure and chemistry of the hydrophobic surfaces found in the Namib beetle has generated scientific interest tremendous learning for their potential applications to humans.
Birds and fossil fuels
Flying and hovering birds are masters of aerodynamic efficiency, and their wingtip feather design inspired engineers to add small ‘wings’ that spin up to reduce drag caused by vortices at the tip of the aircraft’s wings.
By copying this wingtip design, commercial airlines have saved 10 billion gallons of fuel, reducing CO2 emissions by 105 million tons per year.
To sequester this carbon, one would need to plant about 16 million hectares of trees a year – an area larger than the territory of Norway or Japan.
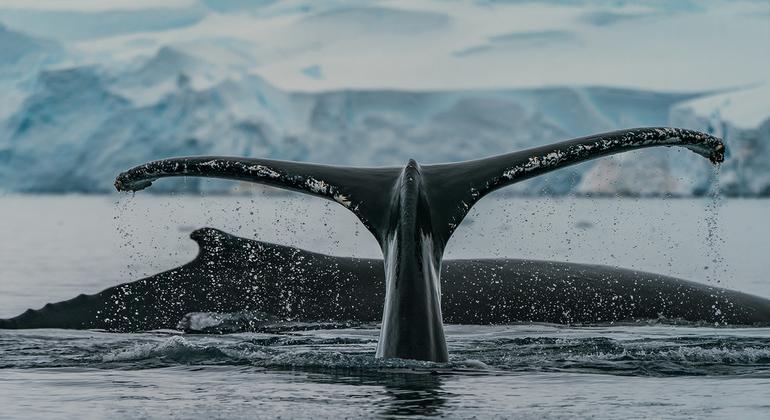

Extinction is not a foregone conclusion
The waste of extinction is perhaps most highlighted by the near-extinction of the humpback whale.
Over-hunting nearly wiped out these giant creatures, one of the largest that ever lived on the planet, and the humpback population dwindled to just 5,000 by 1966.
Conservation organizations and scientists have sparked public and political outcry and humpback whale numbers have rebounded to an estimated 80,000 today. The special feature of the humpback is that there are bumpy ‘bulbs’ in the front of the flippers that help these giants move with extraordinary agility.
Tubers give whales a hydrodynamic advantage – they minimize drag, enhance their ability to maintain motion and, crucially when attacking prey, allow them to turn at sharper angles. Among other uses, they have inspired engineers to build some of the most efficient industrial propellers and wind generators. If the humpbacks were extinct, we might never have been able to take advantage of the bulbous design.
The exceptional organisms outlined above, along with the sustainable engineering designs they have inspired, make a compelling case for why we must conserve biodiversity.
Organisms create the support systems that make all life on Earth, including human life, possible: millions of species are in jeopardy, but the loss of even one species is devastating. can have enormous negative consequences for humanity.
The story is based on the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) booklet, How sustainable engineering solutions depend on biodiversity