Resounding success: NASA asteroid strike leads to a major boost in world-saving test
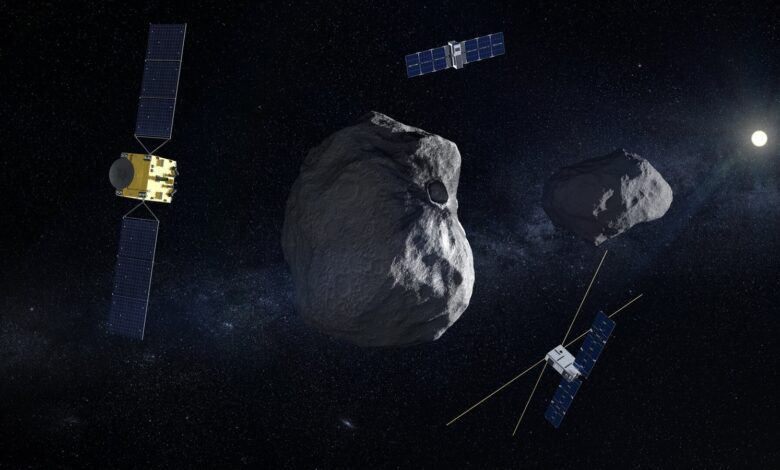

A small, harmless spaceship small planet NASA says millions of miles away has succeeded in shifting its orbit when announcing the results of a world-saving test.
Two weeks ago, the space agency conducted a test to see if in the future a killer rock could be ejected from Earth.
“This mission shows that NASA is trying to be ready for anything The universe throw in we“NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said during a briefing at space agency headquarters in Washington.
The Dart spacecraft crammed a crater into the asteroid Dimorphos on September 26, throwing debris out into space and creating a trail of dust and comet-like wreckage several thousand miles (km) long. ). It’s been several nights in a row telescope Observations from Chile and South Africa to determine how much of the impact altered the path of the 525-foot (160-meter) asteroid around its companion, a much larger space rock.
Before the collision, the moon took 11 hours and 55 minutes to orbit its parent asteroid. Scientists had expected the flyby to take 10 minutes, but Nelson said the impact shortened the asteroid’s orbit by 32 minutes.
“Let’s all take a moment to immerse ourselves in this … the first time humanity has changed the orbit” of a celestial body, said Lori Glaze, NASA’s director of planetary science. Glaze, NASA’s director of planetary science.
Apollo astronaut Rusty Schweickart, co-founder of the B612 Non-Profit Foundation, dedicated to protecting The earth from the asteroid strikes, said he was “obviously delighted, no doubt about it” by the results and attention the mission has brought to the asteroid’s deflection .
The team’s scientists said the amount of debris appeared to play a role in the results. The impact can also make Dimorphos wobble a little, said NASA program scientist Tom Statler. That could affect the orbit, but it will never return to its original position, he noted.
The two bodies were originally less than a mile (1.2 km) apart. They are now tens of yards (meters) closer.
None of the asteroids pose a threat to Earth – and still do not as they continue their journey around Sun. That’s why scientists chose this pair for this important costume rehearsal.
Planetary defense experts prefer to push a threatening asteroid or comet out of the way, given years or even decades, rather than blow it up and create more pieces that can rain down on Earth .
“We really need warning time for a technique like this to work,” said mission leader Nancy Chabot of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, which built the spacecraft and mission management worth $325 million, said.
“You have to know they’re coming,” Glaze added.
Launched last year, the vending machine-sized Dart – short for Double Asteroid Redirection Test – was destroyed when it crashed into an asteroid 7 million miles (11 million km) away at 14,000 mph. hour (22,500 km/h).
Daniel Brown, an astronomer at Nottingham Trent University in the UK, said: “This is a huge feat, not least in taking the first step in being able to protect us from the effects of the Earth’s rays. future asteroids,” said via email.
Brown also said that it was “particularly interesting” that amateur sky photographers could see the tail of the debris with medium-sized telescopes.
The team’s scientists warn that further research is needed to not only identify the countless more space rocks out there, but also to determine their composition – some are solid, while others are piles of bricks. crumbs. For example, reconnaissance missions may be necessary before launching impactors to deflect orbit.
“We shouldn’t be too eager to say one Statler said.
However, he and others are excited about this first attempt.
“We’ve been imagining this for years and it’s finally come true which is actually quite a thrill,” he said.