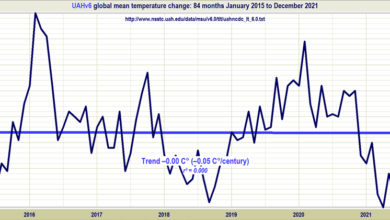
New paper by Henrik Svensmark on Supersaturated Nuclei and Cloud Condensation – Increasing Capacity With That?

Clouds are an essential part of the Earth’s climate system. They play a large role in weather patterns, precipitation, and global temperature regulation. A recent study titled “Saturation and critical size of cloud condensation nuclei in marine Stratus clouds,” published year Geophysical research lettergives us new information about how clouds form, especially over the ocean.
What are cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and supersaturation?
Clouds form when moist air rises and cools. This cooling results in supersaturation, where the air has more water vapor than it can hold. This additional water vapor condenses into small particles called cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), which then grow into cloud droplets. The size and number of these CCNs are important for determining what the clouds will look like.
Traditionally, scientists have assumed that only larger particles (about 60 nm in diameter) can become CCN at typical supersaturation levels (0.2%–0.3%). However, this study by Henrik Svensmark and his team shows that much smaller particles can also act as CCN if the supersaturation is higher than previously thought.
Key findings of the study
- Higher degree of supersaturation: Research shows that marine stratus clouds, especially those off the coast of California, often have supersaturation levels higher than 0.5%, sometimes even up to 1%. This number is much higher than what scientists once believed and suggested that smaller particles (25-30 nm) could act as CCN under these conditions. “On average, supersaturation in marine clouds is significantly higher than the conventional view of 0.2%–0.3%,” the authors write.
- Smaller critical size of CCN: Using satellite data and scientific theories, researchers created maps showing global supersaturation levels and the sizes of particles that could act as CCNs. They found that marine clouds are more sensitive to changes in small particle counts due to higher levels of supersaturation. This means that even smaller particles than previously thought can form cloud droplets. “Higher supersaturation implies a smaller CCN trigger size that makes cloud formation more sensitive to changes in aerosol nucleation,” the study notes.
- Effect on cloud properties: Higher levels of supersaturation mean cloud formation is more dynamic and more sensitive to changes in active particles such as CCN. This can change cloud properties, such as the number of droplets and their thickness, affecting how much sunlight they reflect and how much heat they retain. “Due to the higher saturation, much smaller aerosols are activated into cloud droplets,” the study explains.
How did researchers study this?
The researchers used data from a variety of sources, including satellite observations and aircraft measurements. They analyzed these data to understand the relationship between the number of CCNs and supersaturation.
- Satellite observation: They used satellite data to estimate the number of water droplets in marine stratus clouds. This, along with measurements of cloud thickness and water content, helped them analyze cloud properties over the oceans.
- Aerial measurements: Measurements from aircraft off the California coast were significant in detecting higher-than-expected levels of supersaturation. These measurements provide direct evidence that smaller particles can act as CCN. “Observations of clear-air marine stratus clouds off the California coast reveal a functional relationship between cloud condensation nucleus (CCN) number and supersaturation,” the authors note.
- Simulation: Researchers used computer modeling to simulate how cloud droplets form under different conditions of supersaturation and vertical motion. These simulations support their observations, showing that smaller particles can form cloud droplets at higher supersaturation levels. “Independent support for such high supersaturation in marine clouds comes from CCN measurements provided by the ‘Atmospheric Tomography Mission.’” The study states:
Why is this research important?
This research is important because it changes our understanding of how clouds form. Clouds play an important role in Earth’s climate by reflecting sunlight and trapping heat. Small changes in cloud properties can have large impacts on weather and climate. By showing that cloud formation is more sensitive to smaller particles and higher levels of supersaturation, this study helps us better understand how clouds and aerosols interact.
- Aerosol-cloud interactions: Research shows complexity in how aerosols (tiny particles) and clouds interact. A better understanding of these interactions is important for improving weather and climate forecasts.
- Cloud microphysics: The study emphasizes the importance of the degree of supersaturation in determining cloud properties. This has implications for studying and modeling different cloud types and their role in weather systems.
Conclusion
The study “Supersaturation and critical size of cloud condensation nuclei in marine stratus clouds” by Svensmark et al. provides new insights into how clouds form. By revealing higher-than-expected levels of supersaturation and smaller CCN activation, this study challenges what we thought we knew and opens new doors to understanding Earth’s atmosphere . As we continue to learn more about cloud formation, studies like this are essential to understanding the complexity of our climate.
Cloud formation is a complex process influenced by many factors. This study sheds light on some key aspects of this process, especially in the marine environment, and highlights the importance of continued observation and research to uncover the mysteries of the atmosphere of our planet.
This research is open access and can be read here
H/T Ken Gregory, Science Friend
Related