How ChatGPT-like AI is supercharging humanoid robots
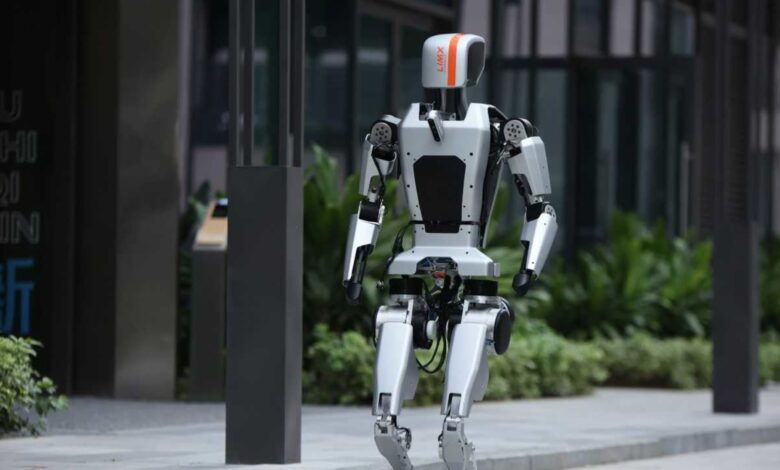

Shenzhen-based LimX Dynamics introduces one of its humanoid robots.
Limx Dynamics
BEIJING – ChatGPT-like artificial intelligence is accelerating research and bringing humanoid robots closer to reality in China, where many of the world’s factories are located.
AI has been around for decades. What has changed with the arrival of OpenAI’s ChatGPT chatbot is the ability of AI to better understand and generate content in a human-like way. Although the US-based tech does not yet have an official presence in China, local companies such as Baidu has released similar chatbots and AI models.
In the field of robotics, the development of generative AI can help machines understand and perceive their environment, said Li Zhang, chief executive officer of Shenzhen-based LimX Dynamics.
About three months after joining the two-year-old startup, Li said he has scaled back his expectations about how long it would take LimX to produce a humanoid robot capable of more than just factory work. but also help households.
Li initially expected the entire process to take eight to 10 years, but now predicts some use cases will be ready in five to seven years. “After working for a few months, I saw the capabilities of many tools improved thanks to AI,” he said in Mandarin, translated by CNBC.
“It has accelerated our entire research and development cycle,” he said.
Companies are rushing to seize the opportunity. OpenAI itself is humanoid robot support starting a businesswhile that of Elon Musk Tesla To be developing separatelycalled Optimus.
electric vehicle giant BYD last year invested in Shanghai-based Agibot just months after its founding, according to PitchBook.
And at a high level, Chinese state media in November published a photo of Chinese President Xi Jinping observing a humanoid robot at an exhibition center during his first trip to Shanghai since the pandemic. Robots already Developed by Fourier Intelligence.
Before humanoid robots reach households, as LimX ultimately intends, factories could be a lucrative, self-contained scenario in which to deploy them.
According to Stanford’s latest report, China surpassed Japan in 2013 to become the world’s largest installer of industrial robots and now accounts for more than 50% of the global total. AI index report.
Electronics, automobiles, metals and machinery are the three leading sectors for industrial robot installations in China, the report said.
Impact on human employment
However, when it comes to completely replacing humans, advances in AI alone are not enough.
LimX’s Li said that even if AI allows robots to think and make decisions on par with humans, mechanical limitations are the main reason why humanoid robots cannot yet replace human labor. People.
One of LimX’s backers, Future Capital, has also invested in a company called Pan Motor that specializes in manufacturing motors for humanoids.
Eric Xia, partner at Future Capital, an investor in LimX, pointed out that innovative AI does not directly help the robot’s movements. But “advances in large language models can help humanoid robots with advanced mission planning,” he said in Chinese, translated by CNBC.
Other LimX investors include Lenovo Capital.
The shift to factory robots could accelerate as costs per robot fall.
Steve Hoffman, president of a startup accelerator called Founders Space, said he is working with a Chinese startup called Fastra, which he hopes can start mass-producing robots. in a year. He said he spent time in China this year teaching local businesses how to integrate AI.
“We have received six orders from research institutions,” he said, noting that the startup aims to reduce the cost per robot to between $50,000 and $100,000 upon deployment. .
“If we can hit the $50,000 price point, we can sell a lot of robots,” he said, pointing out that the robots’ batteries can be charged as they operate, 24 hours a day. “The robot can be paid for in a year.”
In pharmaceutical research, AI can make it possible to reduce costs without cutting human labor.
“You don’t save costs in our business by using less,” said Alex Zhavoronkov, chairman of the board, managing director and CEO of Insilico Medicine, which has offices in Hong Kong. more people. You actually save costs by doing fewer failed tests.” , New York and other parts of the world.
He notes that big pharmaceutical companies often have to spend thousands of dollars to reproduce a molecule for testing — and will run several thousand such tests per program. He confirmed that with the help of AI, Insilico only needs to synthesize about 70 molecules for each program.
The company published a paper in the journal Nature in March claiming to have reached phase 2 clinical trials for a drug. Medicine created by AI.




