IPCC AR6 Report Removed Holocene

By Andy May
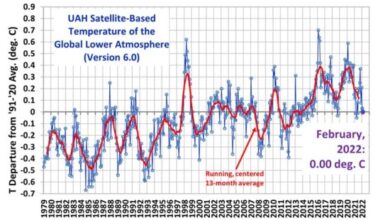
You won’t find much in IPCC Report AR6 about CO . atmosphere2 concentration development during Holocene. They talk a lot about how CO2 concentrations relative to global temperatures in the years since 1850 and over the past 800,000 years, but little in terms of changes since 12,000 years ago. On page 44 of the Technical Summary section, we see the figure below similar to Figure 1.

Figure 1 is designed to mask the relationship between CO2 and global atmospheric surface temperature (GAST), not illuminating it. It was designed to conceal abundant, credible, and well-known evidence that for much of Earth’s history CO2 concentrations decrease as global temperatures increase. Figure 2 from Javier Vinos’ book (Viños, 2022, p. 145). It displays the data in a much clearer and more realistic way.



The AR6 graph tries to imply that the temperature follows CO2 focus and use smart time scales and curated data to make that point. Figure 2 shows all data for the Cenozoic Period using a time scale and shows the opposite to be true. Usually, CO2 and the temperature moves in opposite directions.
The area circled in Figure 1 shows CO2 concentrations were increasing during the Holocene, when temperatures rose about 5 degrees above the last glacial maximum. This crams the entire Holocene into less than a millimeter. AR6 tells us that “the intention of [Figure 1] show that CO2 and temperature covariates, both in the past and in the future…” But the truth about the relationship between them is cleverly hidden in Figure 1 by the design of the figure, the uncanny time scale, and the selected data selection. use. It is not a scientific illustration intended to illuminate the truth; that’s a bit of clever propaganda.
In Chapter 2, they conspire dome C And WAIS share CO . gas2 from 21,000 years ago to 10,000 years ago in a very small cell (AR6, p. 301). It is shown in Figure 3.



Why they avoid showing CO2/temperature relationship in Holocene Epoch? They crammed it into less than a millimeter in Figure 1 and chopped it up in Figure 3. The Holocene is the last 12,000 years, the quality of the data represented for that period should be high, compared to the rest of the Cenozoic. Consider other sources of Holocene CO2 data, like Monnin, 2004.



As Figure 4 shows, CO2 and ONLY4 concentrations (methane) in the atmosphere have increased over the past 5,000 to 6,000 years as representative global temperatures have decreased. This is contrary to the IPCC stated purpose of showing Figure 1. The representative global temperature curve shown in Figure 4 is from Marcot’s representative but reinterpreted by Vinós (Viños, 2022). Both climate model temperature and CO2 concentrations that move inversely to temperatures represent most of the Holocene Epoch.
CO . gas2 The concentrations in Figure 4 are those of Eric Monnin and eleven co-authors (Monnin, et al., 2004) in one study. article IN Letters of Earth and Planetary Science. Their figure 1 is the available Antarctic ice core CO graph2 represents the Holocene, it is shown as our Figure 5. In this graph, the present is on the left and the beginning of the Holocene is on the right, directly opposite the previous figures.



The Dome C ice core shows the entire Holocene. It is drawn in Figure 6, oriented the same as Figures 1 to 3, with the current on the right.



In Figure 7, we compare three temperature reconstructions. We use Vinther refactoring for continent (Vinther, et al., 2009), the Reconstruction of Rosenthal (Rosenthal, Linsley, & Oppo, 2013) from the Trans-Indonesia Route in the Tropical Pacific, and Old Antarctic Dome temperature reproduction (Jouzel, et al., 2007).



Figure 7 shows temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere dropping over the past 5,000 to 6,000 years or so, a period known as the “New Ice Age”. While Reconstruction of Rosenthal Based on ocean temperatures at a depth of 500 meters in Indonesia Throughway between Borneo and Sulawesi, water temperatures are thought to be largely representative of ocean surface temperatures in the tropics and North Pacific. This makes sense as they track Vinther’s Greenland ice core temperatures pretty well.
Antarctica dances to another drummer. It moves against the transparent Northern Hemisphere temperature Holocene climate optimization (circa 8000 BC to 4500 BC) and while the temperature in the Northern Hemisphere dropped after 4,500 BC, the temperature in Antarctica remained constant. After 5000BC CO2 concentration increaseas shown in Figure 6.
Discuss
Renee Hannon noticed the scam plot illustrated in Figure 1 and pointed it out in the comments to my post on Javier’s interview with Tom Nelson. See her comment This. of IPCC stated goal is “to provide governments with levels of scientific information they can use to develop climate policies.” Is cherry picking data and creating scam illustrations “scientific”? Is ignoring and hiding relevant, peer-reviewed, valid data “scientific?” I think not.
I recall one time I was researching a paper for another publication and found that AR6 was trying to discuss the famous Iris Effect (see Thispart Lindzen and Choi), discovered in 2001 by Richard Lindzen, Ming-Dah Chou, and Arthur Hou (Lindzen, Chou, & Hou, 2001) and did so without a single mention of anyone in the series. surname, check for yourself, see pages 972-973 in Chapter 7. They refer to Lindzen, et al., 2001 later in Chapter 7 in a different context, so you’ll find the article in the bibliography of the chapter. Being picky, ignoring contradictory data, “forgetting” to refer to discoverers of key concepts has reached a monumental culmination in this IPCC. I feel so ashamed.
Jouzel, J., Masson-Delmotte, V., Cattani, O., Dreyfus, G., Falourd, S., & Hoffmann, G. (2007). Climate change of the Antarctic orbit and millennia over the past 800,000 years. Science, 317, 793-796. doi:10.1126/science.1141038
Kobashi, T., Severinghaus, JP, Brook, EJ, Barnola, J.-M., & Grachev, AM (2007). Exact timing and characterization of the abrupt climate change 8200 years ago caused by air trapped in polar ice. Quaternary Science Review, 26(9-10), 1212-1222. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.01.009
Lindzen, R., Chou, M.-D., & Hou, A. (2001, March). Does the Earth have adaptive Iris. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Association, 82(3). Taken from https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/bams/82/3/1520-0477_2001_082_0417_dtehaa_2_3_co_2.xml
Monnin, E., Steig, EJ, Siegenthaler, U., Kawamura, K., Schwander, J., Stauffer, B., . . . Fischer, H. (2004). Evidence of a significant cumulative rate shift in Antarctica during the Holocene, through CO . synchronization2 in the Taylor Dome, Dome C and DML ice cores. Letters of Earth and Planetary Science, 45-54. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.05.007
Rosenthal, Y., Linsley, B., & Oppo, D. (2013, 1 November). Heat content of the Pacific Ocean over the past 10,000 years. Science. Taken from http://science.sciencemag.org/content/342/6158/617
Vinos, J. (2022). Climates of the Past, Present, and Future, A Scientific Debate, 2nd Edition. Madrid: Critical Scientific Publishing. Taken from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363669186_Climate_of_the_Past_Present_and_Future_A_scientific_debate_2nd_ed
Vinther, BM, Buchardt, SL, Clausen, HB, Dahl-Jensen, D., Johnsen, SJ, Fisher, DA, . . . Svensson, AM (2009, September 17). Holocene thinning of the Greenland ice sheet. Nature, 461. Taken from http://users.clas.ufl.edu/rrusso/gly6932/vinther_etal_nature09.pdf