Electricity production depends on the weather – Big increase thanks to that?
The basic policy to combat “Climate Change” in the West is to install and heavily subsidize the production of electricity from “renewable” wind and solar. The recorded productivity history of “Renewable” power generation across Europe since 2008 is presented below.
The impact of the 2021 Wind Drought can be clearly seen in terms of the 2021 yield reduction.
Wind and weather-dependent electricity generation in Europe in 2021
Over the past 10 years, when “Renewable” installations have been established in Europe, they have, on average, achieved the percentage of overall productivity as shown below.
Note that generators are typically rated at ~90%, which is the full potential that can be achieved unencumbered by political interventions that favor the mandatory application of input power from ” Renewable energy” depends on the weather.
It is unlikely that any advances in established “Renewable” technologies can yield further substantial improvements from these current mean productivity values.
Gas-fired energy
The most cost-effective, reliable, and incidentally low CO2 emission vehicle using fossil fuels using Natural Gas. Combustion produces:
- CO2 emissions are 1/2 of burning coal or coal
- CO2 emission is almost 1/4 compared to using imported Biomass.
Over the past 20 years, the use of Fracked Natural Gas for power generation, cost-effectively replacing Coal in the United States, has reduced US CO2 emissions per capita by about a third. In the 1990s, the UK’s “Dash for Gas policy” contributed significantly to the UK reducing CO2 emissions by about 40%.
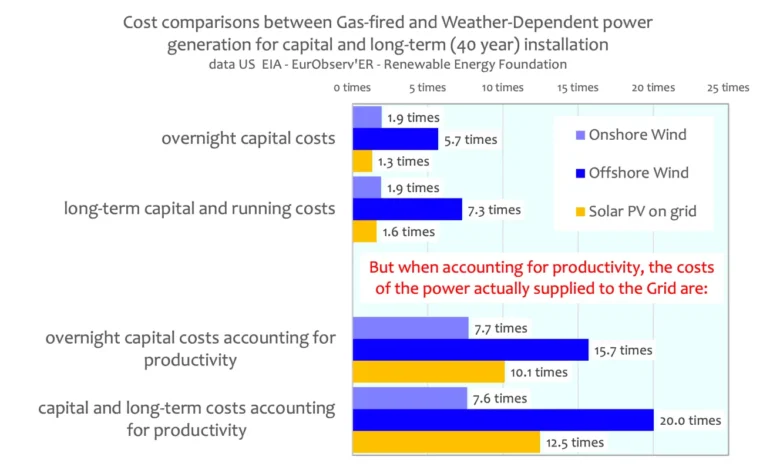
Compare electricity production costs
With the exception of offshore wind power generation, capital base and long-term costs are roughly comparable between fossil fuels and Weather-Dependent generators. However, using gas is particularly cost-effective.
The cost comparison above shows the cost of installing and operating the production technologies: the picture changes radically when the productivity gains of different technologies are taken into account. This then shows the comparative cost of actually supplying a unit of Gigawatt power to the Grid.
Only when their actual capacity to contribute electricity to the grid can the true cost of electricity supplied to the grid be compared: they are summarized below.
So, without taking into account capacity, the US EIA compares electricity generation costs for installation and operation:
- Onshore wind power almost doubles the cost of gas burning
- Offshore wind power is 5-7 times the cost of burning gas.
- Solar power is about 1/2 times the cost of burning gas
But taking into account the yield for the same power output when installing and operating:
- Onshore wind power is ~7 times the cost of burning gas
- Offshore wind power is ~16-20 times the cost of burning gas.
- Solar is about ~10-12 times the cost of burning gas
2020 model of comparative costs for power generation technologies
Any claim that “Renewables” is achieving the same cost as conventional electricity generation is gravely wrong.
These comparative values reveal an irrational political obsession with nominally reducing CO2 emissions, (UK is 1% of Global CO2 emissions), increasing the cost and reliability of how to produce electricity for the country.
Horrible illusion
As Professor David Mackay FRS, (renowned Cambridge physicist and former chief science officer at the UK Department of Energy), said in an interview shortly before his death in 2016, that the promote
“Renewable energy” is driven by “terrifying illusions”.
The illusion has been caused by people who have no understanding of the mathematics, engineering and practicality of Energy technologies.
Has anyone sane ever bought a car that costs 8 to 20 times the normal price that only works one day for five days, when you never know what day it could be? And then emphasize that its technology is used to power the entire economy.
The comparative figures above are an underestimation of the true cost of entrusting weather-dependent “Renewables”. These comparisons take into account only capital and operating cost comparisons of the generating facilities themselves, and the actual power generated taking into account the measured productivity capabilities of each power generation technology. .
Other Cost and Penalty Impacts of “Renewable Energy” CO2 Emissions Depends on the weather
Significant ancillary costs, not taken into account in the calculations above, inevitably also associated with wind power and PV solar generators are due to:
- their unreliability in terms of both power discontinuity and power variability.
- the immutability of Renewable Energy: the wind won’t blow, the clouds won’t go away and the world won’t stop spinning in order, whenever Mankind needs strength.
Weather-dependent generators don’t run 24/7: they don’t reach 90% capacity.
- “Renewables” poor generation times, often not well coordinated with demand: for example, solar power, as recently seen in California, electricity drops in the evening, at a time of demand peak, leading to rolling power outages. Solar energy production in winter is almost non-existent even in Southern European countries, ~1/7 of the output compared to summer, a period of lower electricity demand.
- Long power transmission lines from remote, distributed generators are subject to both power loss during transmission, costly infrastructure and increased maintenance costs.
- requires sterilization of large areas of land, especially when compared with conventional power generation, (gas and nuclear combustion).
- Much additional destructive technical infrastructure is required for access.
- the ongoing cost of back-up generation, which is necessary to maintain an uninterruptible power supply, but can only be used occasionally and has to run wastefully in spinning reserves and emits a CO2 number.
It should be noted that if there must be enough backup capacity by using fossil fuels to support the grid whenever wind and solar power are not available. Such support is expensive when running continuously, then there is little point in doubling generation capacity, available 24/7, with generators Relatively poor weather dependence much more efficient and costly, can displace some CO2 emissions but they certainly still emit significant CO2 levels to manufacture, install and maintain.
Comparison of Performance and Cost of Power Generation Technologies: 2020
- any consideration about battery-powered electricity storage, which will lead to very significant additional costs, is long-term battery storage, (just a few days), even economically feasible. This makes any idea of long-term seasonal electricity storage impractical.
- Asynchronous generators lack the inherent inertia needed to maintain grid frequencies.
- Weather-dependent generators failed to recover from a “black start” following a major grid outage.
In addition, it is important that these cost analyzes do not take into account:
- The inevitable environmental destruction and wildlife devastation caused by Weather Dependent generators.
- The ‘carbon footprint’ of technologies creates Weather Dependent: they may never save much CO2 over their lifetime as they are likely to require for the source material, production, installation, maintenance and finally demolition.
- When viewed as a whole, all these installations are entirely dependent on the use of significant amounts of fossil fuels as raw materials and fuel for production.
- technologies used in generators Weather dependence is also heavily dependent on large quantities of scarce materials giving rise to huge mining demands.
- Energy Return on Energy Invested: Weather-dependent generators can generate only a minimal amount of excess energy over their promised service life for initial production and installation. head. They certainly do not provide a large amount of excess energy often enough to support the diverse needs of a developed society. Accordingly, they are parasitic on the use of fossil fuels for their existence.
There are no imposed additional costs assessed in the Compare Costs section above.